
Anxiety disorders are linked to higher-than-normal levels of cortisol in the blood.Ĭorticosteroids regulate many parts of the body's response to stress, including the immune system, the hippocampus (a part of the brain important in learning and memory), the hypothalamus (which controls appetite, temperature, sleep patterns, and other aspects of physiology), and the pituitary gland (which controls the release of other hormones). Stress increases this amount dramatically - up to 20 mg/day for some people. Too much cortisol can be toxic to the body, so normal people produce about 2-4 mg of cortisol per day. It also controls blood sugar levels by regulating the release of insulin from the pancreas and preventing the liver from storing too much glucose. The adrenal cortex produces glucocorticoids such as: Hydrocortisone: Cortisol, as it is often known, governs how the body transforms fats, proteins, and carbs into energy. The adrenal cortex is responsible for the production of two types of corticosteroid hormones: glucocorticoids and mineralcorticoids.
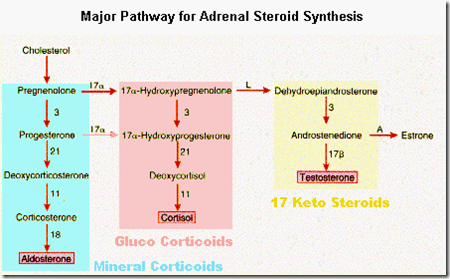
What is the major glucocorticoid of the adrenal cortex?
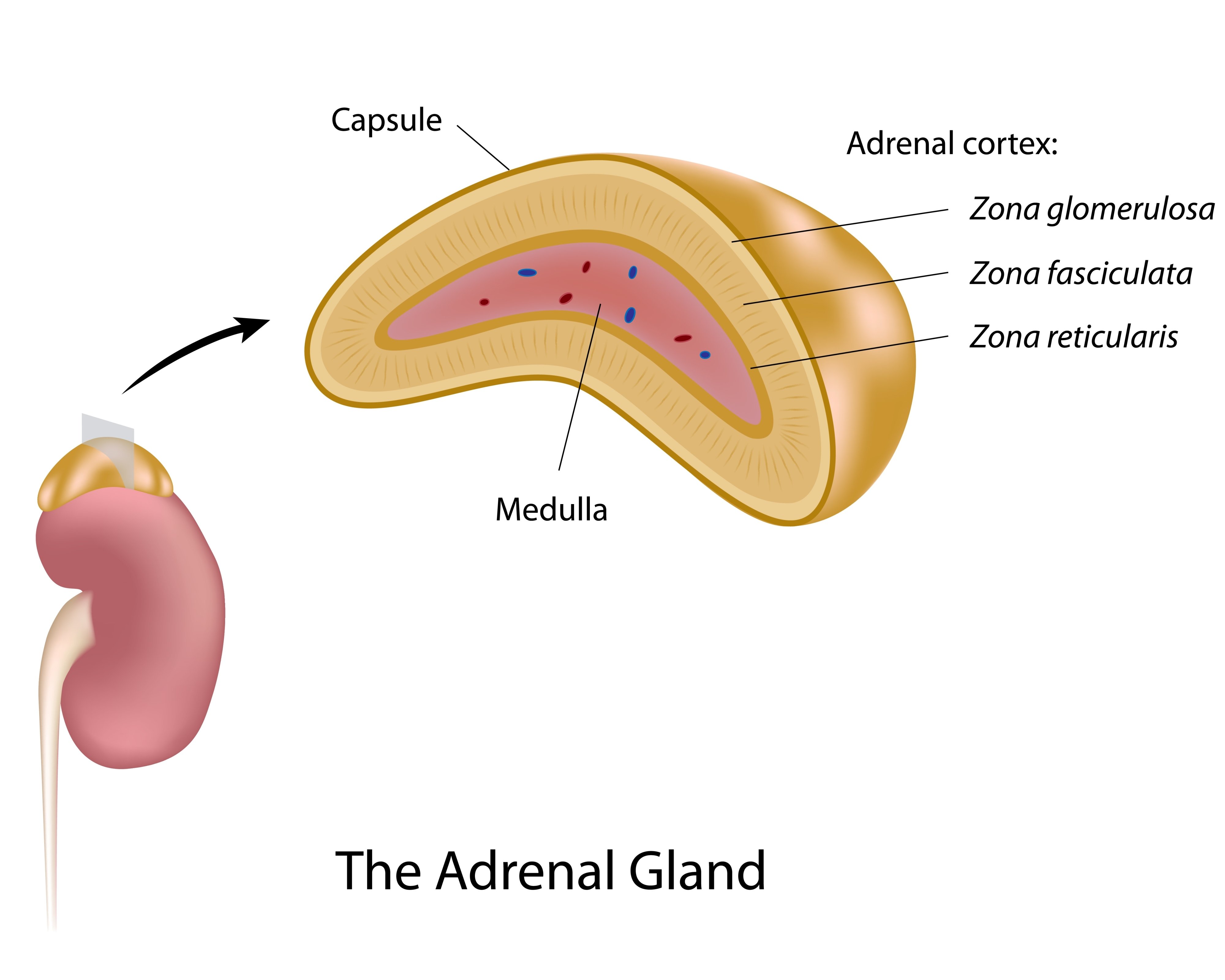
They include testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT - a form of testosterone). However, for people who have low nutrient intakes due to poor eating habits, adding cortisol to their diets could help increase their intake of certain nutrients such as zinc and B vitamins.Īndrogens are male hormones that control development and reproduction. Taking cortisol supplements may not be beneficial if you are already receiving adequate nutrition from food. Stress can cause your body to release large amounts of cortisol which is why people often feel tired after a stressful event such as a car accident or fight. They are also responsible for regulating blood pressure, storing energy, and influencing behavior. Corticosteroids are natural substances that reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
The adrenal glands produce two types of hormones: corticosteroids and androgens. Estrogen controls reproductive functions such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Androgens influence growth and development as well as sexual characteristics. Cortisol regulates many aspects of body function, including stress response, inflammation, blood glucose levels, and fat storage. Aldosterone aids the kidneys in controlling the quantity of salt in the blood and tissues. Aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid), cortisol (a glucocorticoid), androgens, and estrogen are the most significant (sex hormones). Several hormones are produced by the adrenal cortex.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
